Are you curious about the fascinating world of biogas digesters and their costs? Look no further! In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of methane digester technology, including its definition, working principle, and the economic advantages it presents.
Biogas digesters, also known as anaerobic digesters, are environmentally-driven systems that harness the power of microorganisms to decompose organic waste materials, such as food scraps, agricultural residues, and livestock manure, in an oxygen-free environment. As these organic materials break down, they produce a combination of gases, the primary one being methane.
This technology has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits. Biogas digesters not only minimize the harmful release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, but they also produce a valuable byproduct called biogas.
This biogas, comprising mostly methane, can be captured and utilized as a renewable fuel source for electricity generation, heat production, and even as a vehicle fuel.
Now, let’s dive into the cost aspect. The initial investment required to set up a methane digester may vary depending on the scale and complexity of the system.
Factors influencing the cost include the digester’s capacity, design, construction materials, and additional equipment needed for gas collection and utilization.
Despite the initial investment, studies have shown that biogas digesters can offer substantial cost savings in various sectors, including agriculture, wastewater treatment, and landfills, along with contributing to a more sustainable planet.
In conclusion, as we explore the financial side of methane digesters, we will gain a deeper understanding of their long-term economic benefits and their role in building a greener future.
Note that we’ll use biogas and methane to mean the same thing. And so join us on this journey to uncover the cost-effective potential of biogas digester technology!
Table of Contents
Anaerobic Digestion: A Key Component of Biogas Digester Systems
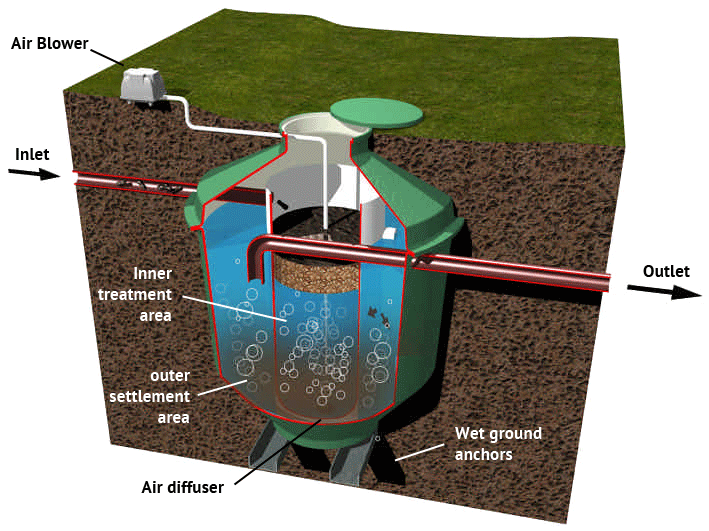
As we delve deeper into the world of biogas digester systems, it becomes clear that anaerobic digestion plays a vital role in their operation.
Understanding the process of anaerobic digestion and its importance in reducing methane gas emissions is crucial in comprehending the cost dynamics of these systems.
Explanation of Anaerobic Digestion Process
Anaerobic digestion is a natural biological process where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Inside a biogas digester system, this process takes place in an enclosed environment, such as a tank or basin.
The organic waste, which can be sourced from various agricultural, industrial, or municipal activities, is fed into the digester.
The microorganisms then break down this waste into biogas, primarily methane, and digestate, a nutrient-rich byproduct.
Read More on How can I make a simple biogas digester at home?
Importance of Anaerobic Digestion in Methane Gas Emissions Reduction
One of the most significant benefits of anaerobic digestion is the reduction of methane gas emissions. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas with a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide.
By capturing and utilizing the methane produced through anaerobic digestion, biogas digester systems help combat climate change and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Additionally, the process of anaerobic digestion helps minimize odors, pathogens, and other potential environmental pollutants that may be present in organic waste. This further enhances the environmental benefits of methane digester systems.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Anaerobic Digestion
The cost of anaerobic digestion can vary depending on several factors. These include:
- The size and capacity of the methane digester system
- The complexity of the system design
- The type and characteristics of the organic waste being processed
- The availability and cost of equipment and technology
- The level of expertise required for operation and maintenance
Costs Associated with Methane Digester Systems
Biogas digester systems offer several benefits, but it’s essential to consider the costs involved. From operational expenses to maintenance requirements, understanding the financial aspects is crucial.
Here’s a breakdown of the costs associated with biogas digester systems:
A. Breakdown of Operational and Maintenance Costs
1. Labor costs: Labor is a significant expense in operating and maintaining biogas digester systems. Skilled personnel are required for efficient system management, including monitoring, troubleshooting, and managing the overall operation.
2. Energy or fuel expenses: Depending on the specific digester system, energy or fuel costs can vary. While some systems may utilize the biogas produced as a fuel source, others may require additional energy for heating, stirring, or other processes.
3. Waste feedstock costs: The cost of waste feedstock, which serves as the input material for the digester system, can vary. It depends on factors such as availability, transportation, and preparation of feedstock, whether it’s agricultural residues, food waste, or other organic materials.
4. Regular maintenance requirements: Methane digester systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent any potential issues. Maintenance costs include equipment inspections, repairs, and replacement of components.
Understanding the breakdown of these costs is essential for evaluating the overall financial feasibility of biogas digester systems.
However, it’s equally important to assess the return on investment and consider the impact of policy, incentives, scale, and ongoing research and development efforts on cost dynamics.
Read More on Biogas: The Good And The Not-So-Good Part You Need To Know
Costs of Biogas Digester in General
The capital cost of an on-farm biogas digester ranges from approximately $400,000 to $5,000,000. This depends on the size of the operation and technology used, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency AgSTAR.
The average on-farm biogas digestion unit costs around $1.2 million. The cost of a unit varies depending on its size, design, and features.
The type of biogas digester required for your operation, and its cost, vary depending on the number of livestock.
Similarly, most digesters are somewhat customized by the provider, so capital outlay and operating and maintenance costs vary.
You must also consider annual operation and maintenance costs, repairs, parts, labor, and insurance. This is important when calculating the cost of a biogas digestion system, annual operation, and maintenance costs.
You must thoroughly understand the variables of any funding programs before continuing to invest in a system. This is important since biogas digesters are capital-intensive,
It would help if you spoke with an agricultural loan officer about any loan risk associated with a methane digester to ensure that the additional debt will not jeopardize your ability to access capital for your operation.
Determine the extent to which you will offset costs by generating revenue or reducing energy expenditures over the life of the digester as part of the economic analysis. Utility contracts can vary significantly between rural communities.
Some utilities have net metering policies that allow small energy generators, such as those equipped with a biogas digester, to offset their energy consumption by producing electricity. However, the value will differ depending on the utility.
Assessing the Return on Investment (ROI) of Methane Digester Systems
Implementing methane digester systems can have a significant impact on a business’s bottom line. Assessing the return on investment (ROI) is crucial to determining the economic viability of adopting these systems.
A. Calculating ROI for Methane Digester Implementation
Calculating the ROI for methane digester implementation involves a comprehensive analysis of costs and potential returns.
It considers the initial investment required, operational costs, and the projected income generated from the digester system.
By examining these factors, businesses can determine the financial benefits of investing in methane digesters.
B. Evaluation of Payback Periods
The payback period is another important metric used to assess the ROI of biogas digester systems. It represents the time it takes for the initial investment to be recovered through operational savings or revenue generation.
Businesses can use this information to gauge how quickly they can recoup their investment and start benefiting financially from the digester system.
Read More on The Best Amount Of Gas A Biodigester Can Give You
C. Analysis of the Economic Viability of Adopting Methane Digester Systems
In addition to ROI and payback periods, a thorough analysis of the economic viability of adopting methane digester systems is essential.
This analysis considers factors such as tax incentives, grants, and subsidies available for implementing these systems. It also evaluates the potential cost savings from reduced waste management expenses and energy generation.
By assessing these economic factors, businesses can make informed decisions about the financial benefits of methane digester systems.
Policy and Incentives: Impact on Methane Digester Cost Dynamics
In order to understand the cost dynamics of methane digester systems, it is crucial to take into account the various government policies, regulations, and incentives that impact these costs.
A. Government Policies, Regulations, and Incentives Influencing Costs
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the costs associated with biogas digester systems.
For instance, the implementation of stringent environmental regulations can increase compliance costs for digester operators, impacting the overall system cost.
On the other hand, government incentives like subsidies and grants can help reduce the initial investment required for setting up a methane digester system.
These incentives can provide financial support to farmers or project developers, making the adoption of these systems more economically viable.
B. Discussion of Renewable Energy Incentives and Carbon Credits
Renewable energy incentives have a direct impact on the cost dynamics of biogas digester systems. In many jurisdictions, renewable energy certificates (RECs) or feed-in tariffs are available for electricity generated from biogas.
These incentives can offset the operational costs of the digester system, reducing the overall cost burden on operators.
In addition, carbon credits can provide an additional revenue stream for operators of methane digester systems.
By capturing and utilizing methane, these systems contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This emission reduction can be quantified and sold as carbon credits in carbon markets, providing a financial benefit that can offset system costs.
Read More on Total Amount Of Useful Gas A Bio-digester Can Produce
C. Tax Benefits and Grants Supporting the Implementation of Methane Capture Technologies
Another important aspect to consider when assessing the cost dynamics of methane digester systems are the tax benefits and grants available to support their implementation.
Many governments offer tax incentives such as accelerated depreciation or tax credits for investing in renewable energy projects, including methane digesters. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs and improve the return on investment for operators.
Furthermore, grants and funding programs specifically targeting methane capture technologies can provide financial support for research, development, and implementation of these systems.
By reducing the financial burden, these grants encourage wider adoption and contribute to further cost reductions.
Scale and Capacity: Cost Variations in Methane Digester Systems
When it comes to methane digester systems, costs can vary significantly depending on the scale and capacity of the system.
Understanding these variations can help stakeholders make informed decisions about the most cost-effective solution for their needs.
A. Comparison of Costs Between Small-scale On-farm Digesters, Community-scale Systems, and Larger Industrial-scale Biogas Plants
One of the primary factors influencing the cost of biogas digester systems is the scale at which they are implemented.
Small-scale on-farm digesters, which are designed to process waste from a single farm, tend to have lower upfront costs compared to larger community-scale systems or industrial-scale biogas plants.
Community-scale systems, which are designed to serve a specific community or group of farms, require additional infrastructure and have higher installation and maintenance costs.
Similarly, larger industrial-scale biogas plants, which are designed to process waste from multiple sources, have higher capital costs but can potentially provide more significant energy production and revenue streams.
Read More on Are Container Homes Legal in Miami? Find Out the Facts!
B. Exploration of Cost-effectiveness Based on Different System Sizes and Capacities
The cost-effectiveness of methane digester systems heavily depends on the size and capacity of the system. Smaller systems may have lower upfront costs but produce less biogas and generate fewer cost savings.
On the other hand, larger systems can have higher capital costs but offer greater potential for energy generation and financial returns.
- Small-scale systems typically have lower installation costs and are suitable for farms with limited waste production.
- Medium-scale systems may require more significant investments but have the potential to offset a substantial portion of the energy needs for a community or group of farms.
- Large-scale systems often involve complex engineering and higher capital costs but can provide significant benefits, particularly for industrial operations or municipalities.
By considering the specific waste production, energy demands, and long-term goals of a project, stakeholders can assess the cost-effectiveness of different system sizes and capacities.
Research and Development Efforts: Reducing Costs Associated with Methane Digesters
Ongoing advancements in digester design:
Researchers and engineers are continuously working on improving the design of methane digesters. By employing more efficient and cost-effective construction materials, such as precast concrete or high-density polyethylene, the upfront costs of building biogas digesters can be significantly reduced.
Additionally, innovative designs that optimize the flow of biogas and maximize methane production are being developed, leading to higher overall efficiency and lower operating costs.
Improved feedstock processing techniques:
Efforts are being made to develop more efficient feedstock processing techniques. This includes the use of pre-treatment technologies that can break down complex organic materials into simpler compounds, making them more easily digestible for microorganisms.
By improving feedstock processing, the methane production rate can be increased, leading to higher revenue generation and quicker return on investment.
Innovations in biogas purification technologies:
Another area of research and development involves the purification of biogas. Traditional biogas purification methods such as water scrubbing or pressure swing adsorption can be expensive and energy-intensive.
However, researchers are exploring newer and more cost-effective purification technologies, such as membrane separation and selective adsorption, which can reduce the overall cost of biogas purification and increase its usability for various applications.
Environmental Benefits and Cost-Effectiveness of Methane Digesters
Methane digesters offer several environmental benefits and have proven to be cost-effective solutions for waste management.
Through the anaerobic digestion process, methane gas emissions can be significantly reduced, leading to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
A. Discussion on Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the primary environmental benefits of methane digesters is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is captured and converted into energy through the digestion process.
By harnessing methane as a renewable energy source, biogas digesters help to mitigate climate change by reducing the release of methane into the atmosphere.
Read More on Shipping Container Homes In Arizona: Stylish And Affordable
B. Waste Management Improvements
Methane digesters also provide significant improvements in waste management. By diverting organic waste, such as food waste and agricultural residues, methane digesters prevent the release of methane gas that would otherwise be emitted from landfills or stored animal waste.
This not only reduces odor and potential contamination of local water sources but also eliminates the need for traditional waste management practices, resulting in cost savings for farmers and businesses.
C. Contributions to Sustainability Goals
Biogas digesters contribute to the achievement of sustainability goals at various levels. At the local level, they help communities achieve waste reduction targets and promote circular economies by converting organic waste into useful energy.
At the regional and national levels, the widespread adoption of methane digesters can contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and increasing the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix.
D. Comparison of Environmental Benefits Versus Costs
When assessing the cost-effectiveness of methane digesters, it is crucial to consider the environmental benefits they provide.
While there may be upfront costs associated with the installation and maintenance of methane digesters, the long-term environmental benefits, such as greenhouse gas reductions and improved waste management, often outweigh these costs.
Moreover, there are various funding options, grants, and incentives available that can further reduce the financial burden of adopting biogas digester systems.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biogas digesters contribute to reducing the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
- Improved waste management: Methane digesters prevent the release of methane from organic waste, leading to improved waste management practices and cost savings.
- Contribution to sustainability goals: Biogas digesters support the achievement of sustainability goals by promoting waste reduction and renewable energy use.
- Cost-effectiveness: Despite initial investment costs, the long-term environmental benefits of methane digesters make them a cost-effective solution for waste management.
Case Study: The Cost of Methane Digester Systems in California Dairy Farms
As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, methane digester systems have gained significant attention as an effective method for capturing and utilizing methane gas produced by dairy farms.
A biogas digester system not only helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also offers potential cost savings for dairy farmers. In this case study, we delve into the cost dynamics of methane digester systems in California dairy farms.
Analysis of the Specific Cost Factors in California Dairy Farms
When assessing the cost of methane digester systems in California dairy farms, several key factors come into play.
Firstly, the initial investment includes the cost of purchasing and installing the digester equipment, as well as any necessary modifications to existing infrastructure.
Additionally, labor and construction expenses, as well as permitting and engineering fees, contribute to the overall cost.
Another crucial factor to consider is maintenance and operational costs. Routine maintenance, repairs, and the expense of sourcing and storing inputs like feedstocks and additives can significantly impact the total cost of operating a biogas digester system.
Furthermore, the cost of electricity needed to run the system and any grid connection fees need to be accounted for to accurately assess the overall cost.
Comparison of Costs in Relation to Dairy Farm Size and Production Levels
It’s important to note that the cost of implementing a methane digester system can vary depending on the size and production levels of the dairy farm.
Larger farms often benefit from economies of scale, as they can distribute fixed costs more efficiently across a higher volume of milk production. Smaller farms may face higher per-unit costs due to the reduced scale of operations.
Additionally, the availability of feedstocks plays a significant role in cost variation. Farms with access to abundant and low-cost organic waste sources such as manure or food waste can potentially lower their overall digester system costs.
In contrast, farms that have limited access to suitable feedstocks may incur higher costs in sourcing and transporting feedstock materials, affecting the cost-effectiveness of the system.
To accurately assess and compare costs, a comprehensive analysis must take into account the specific circumstances and characteristics of each dairy farm.
Read More on Shipping Container Homes in Oregon: Sustainability And Style
The Value Proposition: Weighing Costs and Benefits of Methane Digester Systems
When considering the adoption of methane digester systems, weighing the costs and benefits is crucial to making an informed decision.
Understanding the value proposition of these systems goes beyond purely financial considerations; it encompasses long-term environmental benefits and the potential for a sustainable future.
Summary of the Overall Cost Analysis and Environmental Benefits
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of costs, it is essential to highlight the environmental benefits that methane digester systems offer.
These systems effectively capture and convert methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas, into renewable energy. By doing so, they significantly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Furthermore, the use of methane digesters helps in mitigating odors, minimizing pathogens, and managing waste more efficiently.
These benefits not only contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment but also promote better management practices in various industries.
Now let’s focus on the cost analysis. The initial investment cost for biogas digester systems can vary depending on factors such as scale, capacity, and technology.
On average, the installation cost ranges from $500,000 to $3 million, depending on the size of the operation. Although this may seem substantial, it is important to consider the potential Return on Investment (ROI) over time.
Recommendations for Potential Adopters of Biogas Digester Systems
For potential adopters of methane digester systems, a thorough assessment of various factors is vital. Here are some recommendations to guide decision-making:
- Evaluate your waste management goals: Determine how effectively a methane digester system aligns with your waste management objectives. Are you solely focused on reducing methane emissions or interested in generating renewable energy as well?
- Consider the scale and capacity: Analyze your operation’s size and waste output to identify the appropriate scale and capacity of the methane digester system. Matching the system’s capabilities with your needs is crucial for optimizing benefits and minimizing costs.
- Explore available policies and incentives: Stay informed about government policies and incentives, as they can significantly impact the economic feasibility of methane digester systems. Incentives such as tax breaks, grants, and renewable energy credits can help offset upfront costs and accelerate ROI.
- Stay updated on research and development efforts: Monitor advancements in methane digester technologies and ongoing research to identify potential cost-saving opportunities. As innovation progresses, costs associated with biogas digesters are likely to decrease, making them even more attractive investments.
By carefully considering the value proposition of biogas digester systems, stakeholders can make informed decisions that balance economic costs, environmental benefits, and long-term sustainability.
The integration of these systems contributes not only to a cleaner and more efficient waste management process but also to a greener and more sustainable future for generations to come.
Read More on Shipping Container Home In Louisiana: How To Build One

