When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels play a crucial role. They are the backbone of solar energy systems and understanding the different types can make a significant difference in maximizing efficiency and savings.
Table of Contents
Monocrystalline Panels

Monocrystalline panels are renowned for their efficiency and sleek appearance. Made from a single crystal structure, they are highly efficient in converting sunlight into electricity, making them ideal for situations with limited roof space or lower sunlight exposure.
Additionally, their durability and long lifespan make them a worthwhile investment in the long run. However, their higher cost may deter some budget-conscious homeowners.
Read More on Different Types of Solar Panels: Know Them All!
Polycrystalline Panels
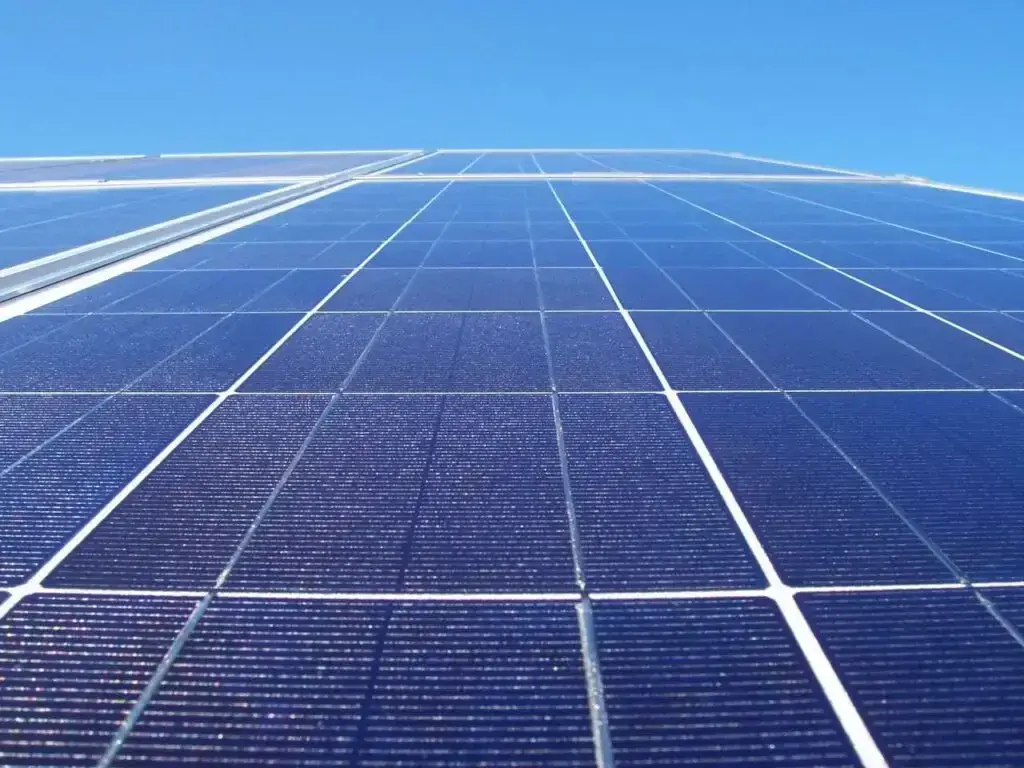

Polycrystalline panels, also known as multicrystalline, have a distinctive appearance due to their multiple crystal structures. They are a cost-effective alternative to monocrystalline panels while still offering decent efficiency levels.
With lower manufacturing costs, they are suitable for those looking for affordable solar solutions. However, they do have a slightly lower overall efficiency and can be less aesthetically pleasing compared to their monocrystalline counterparts.
Read More on Advantages And Disadvantages Of Solar Energy You Didn’t Know About
Thin Film Panels
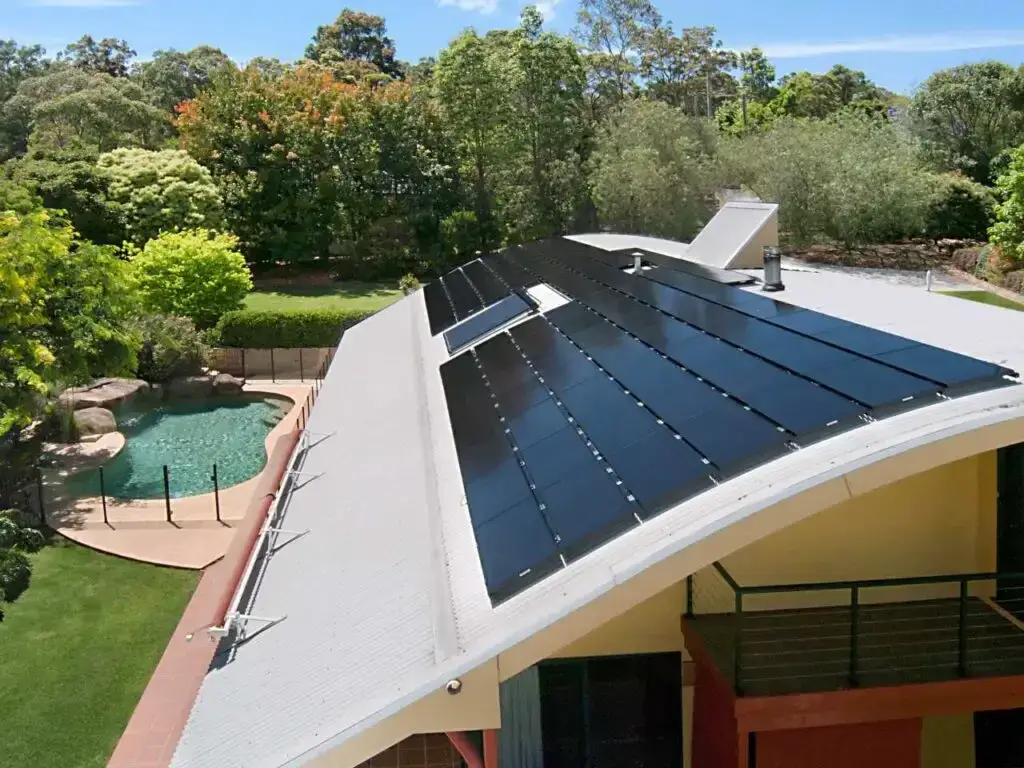

Without doubt, thin film panels are incredibly versatile and can be integrated into various surfaces such as roofs, windows, or even building facades. They are known for their lightweight and flexible nature, making them easier to install and perfect for non-traditional solar panel applications.
These panels also perform well in low-light conditions and have a relatively low production cost. However, they have lower efficiency rates compared to crystalline panels and may require larger surface areas to generate the same amount of electricity.
Bifacial Panels

Bifacial panels, as the name suggests, have the ability to generate electricity from both sides. This unique feature allows them to capture sunlight from above and reflected light from below, making them highly efficient, especially in settings with high albedo surfaces or in dual-axis tracking systems.
Bifacial panels can also enhance overall energy production and provide more design flexibility. However, their higher upfront costs and complex installation requirements may not be suitable for every solar project.
Now that you have a comprehensive overview of the different types of solar panels, their advantages, and disadvantages, you can make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the right panels for your energy needs.
Whether it’s monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin film, or bifacial panels, harnessing the power of the sun has never been more accessible.
Read More on Are Solar Panels Worth The Investment? Here’s The Truth
Solar Panel Installation
Installing solar panels on your property is an important step towards harnessing clean and renewable energy. The installation process involves several key steps that ensure the optimal setup and performance of your solar energy system.
1. Site Assessment
Before installing solar panels, a site assessment is conducted to evaluate the suitability of your property for solar energy generation. Factors such as roof orientation, shading, and available space are taken into consideration.
2. System Design
Once the site assessment is complete, a customized system design is created for your specific solar panel installation. This design takes into account your energy needs, budget, and other factors to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
3. Permits and Regulations
Obtaining necessary permits and complying with local regulations is a crucial part of the solar panel installation process. This ensures that your installation meets safety, zoning, and building code requirements.
4. Mounting Options
There are various mounting options available for solar panels, depending on the type of roof or structure. Common mounting methods include roof-mounted, ground-mounted, and pole-mounted systems.
5. Wiring Setup
The wiring setup connects the solar panels to the inverter and electrical system of your property. Proper wiring is essential to ensure the safe and efficient transfer of electricity generated by the panels.
By following these steps and working with experienced professionals, you can have a successful solar panel installation that maximizes energy generation and contributes to a greener future.
Read More on High Efficiency Solar Panels: Expert Comparison And Costs
Solar Panel Efficiency and Performance
When it comes to solar panel efficiency and performance, there are several factors that can greatly impact how well your panels will perform and generate electricity.
Sunlight Exposure
The amount of sunlight your solar panels receive is crucial for their efficiency. Ideally, the panels should be installed in a location where they can receive maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day. This ensures that they can generate the maximum amount of electricity possible.
Temperature Variations
Temperature can also affect the performance of solar panels. While cold temperatures can actually improve their efficiency, extremely hot temperatures can cause a decrease in performance.
It is important to consider the impact of temperature variations on your solar panels, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Shading
Shade from nearby structures or trees can significantly reduce the efficiency of your solar panels. It is essential to ensure that your panels are installed in an area where they can receive unobstructed sunlight throughout the day. Any shade, even if it is only partial, can result in a decrease in overall energy production.
Tracking Systems
Tracking systems can help optimize the efficiency of your solar panels by automatically adjusting their position to track the movement of the sun. These systems allow the panels to always face towards the sun, maximizing the amount of sunlight they receive.
While tracking systems can increase efficiency, they can also add to the upfront cost of your solar panel installation.
Read More on 11 Greatest Solar Tech Advancements Of 2023
Degradation Over Time
Over time, solar panels may experience a slight decline in their efficiency due to natural degradation. This is a normal phenomenon and is taken into account by manufacturers when providing performance warranties for their solar panels.
It is important to consider the degradation rate and warranty of your panels when choosing the right system for your needs.
Solar Panel Maintenance
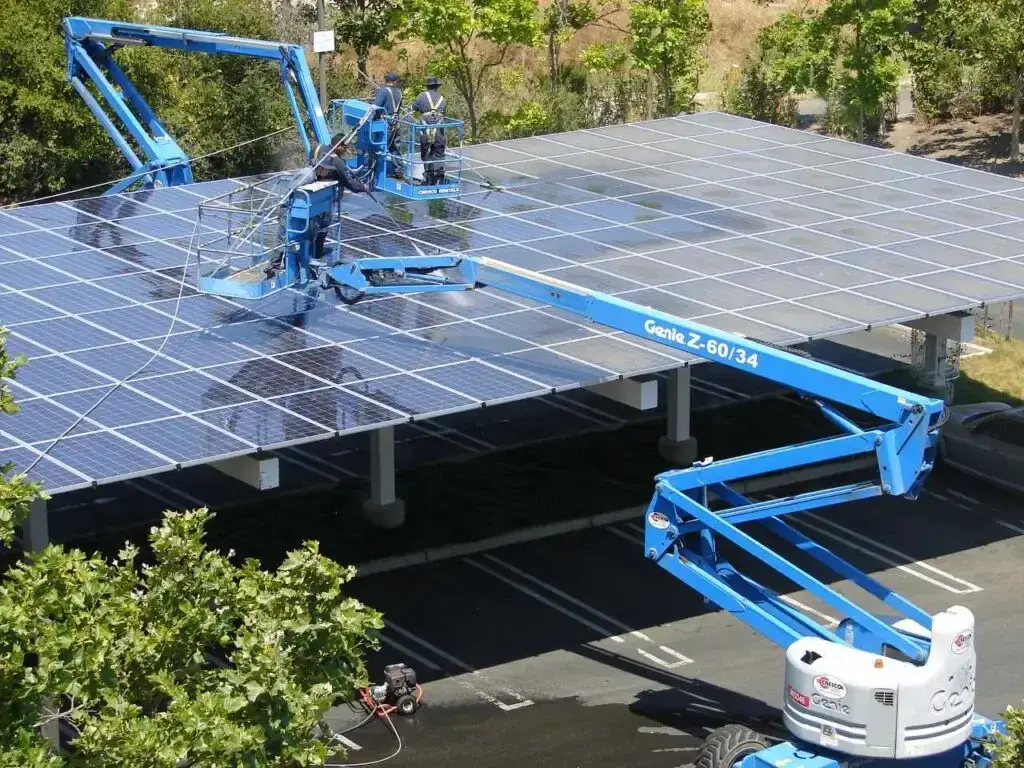

Proper maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your solar panels. By following these maintenance tips, you can maximize the efficiency of your solar energy system:
1. Cleaning
Regular cleaning is important to remove any debris, dirt, or dust that may accumulate on the surface of the solar panels. This can be done using a soft brush or a cloth with non-abrasive soap and water. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals, as they can scratch or damage the panels.
2. Inspection
Periodically inspect your solar panels for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or loose connections. Additionally, check for any shading caused by nearby trees or structures that may reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the panels.
3. Monitoring Systems
Many solar panel systems come with monitoring devices that allow you to track the performance and energy production of your panels. Regularly monitor these systems to identify any abnormalities or drops in performance, which may indicate a potential issue.
4. Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you notice a decrease in energy production or any other issues with your solar panels, there may be common problems that you can troubleshoot.
These can include faulty wiring, loose connections, or issues with the inverter. It is recommended to consult a professional if you are unsure how to fix these issues.
In conclusion, regular maintenance and care are crucial for keeping your solar panels running efficiently and generating optimal energy. By following these maintenance practices, you can enjoy the benefits of solar panels for many years to come.
Read More on Why Container Shortage Compromise Global Logistics And Trade
Solar Panel Benefits and Savings
Switching to solar energy through the installation of solar panels not only offers numerous environmental advantages, but it also brings several significant benefits and savings to homeowners.
1. Reduction in Electricity Bills
One of the most noticeable benefits of solar panels is the reduction in electricity expenses. By harnessing the power of the sun, homeowners can generate their own clean and renewable energy, significantly reducing their dependence on the grid. This ultimately leads to lower monthly electricity bills and long-term savings.
2. Environmental Benefits
Solar panels produce electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases, making them an environmentally-friendly energy solution.
By choosing solar energy, homeowners can contribute to a cleaner and greener planet, reducing their carbon footprint and helping combat climate change.
3. Potential Tax Incentives
In many countries, including the United States, homeowners who install solar panels are eligible for various tax incentives and rebates. These incentives can significantly offset the initial cost of installation, making solar panels a more affordable option for homeowners.
4. Overall Return on Investment
Investing in solar panels typically offers a high return on investment. Not only will homeowners save on electricity bills, but also solar panels often increase property value. In addition, with the ever-rising cost of traditional energy, the savings generated from the panels can be substantial over the system’s lifetime.
By embracing solar energy and taking advantage of these benefits, homeowners can not only save money but also contribute to a sustainable future.
Read More on Best Poolside Container Plants – Stunning Pool Area Choices
Solar Panel Components
When it comes to solar panels, understanding the different components is crucial. Each component plays a vital role in harnessing the power of the sun and converting it into usable electricity. Here are the key components you need to know:
1. Solar Cells
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are the heart of solar panels. These cells are made of semiconductor materials that absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. They are typically made of silicon, which is a highly efficient material for capturing solar energy.
2. Inverters
Inverters are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses. They ensure that the electricity generated by the panels can be used by various appliances and devices.

- Solar hybrid charger inverter with 3000W 24V pure sine wave power inverter and 60A MPPT solar controller in one.
- Suitable for off-grid solar systems, RVs, boats, and yachts.
- An LCD display built inside the unit monitors solar energy input, inverter output power, and battery status.
- A 3000W pure sine wave inverter built into the unit provides reliable, clean, and efficient power.
- Overload and over-temperature protection, as well as auto restart.
- Maximum solar power efficiency is achieved with a 60A MPPT solar controller.
- In-built battery charger for 12V/24V lead-acid and lithium batteries.
- Simple to set up and use, with a USB connector for charging your mobile devices.
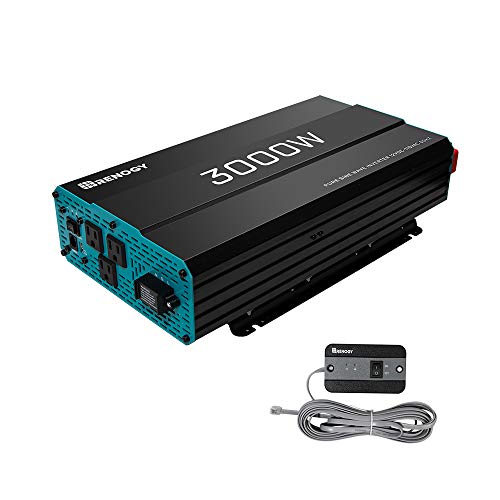

- Renogy 3000W Pure Sine Wave Inverter: Converts 12V DC to 120V AC for dependable power in homes, RVs, trucks, off-grid solar systems, and other applications.
- A 5V/2.1A USB port is built-in for charging your electrical gadgets.
- An AC hardwire port for connecting to an alternating current power source, as well as a remote controller for remote monitoring.
- Heavy-duty aluminum alloy housing for efficient cooling and robust shock and dust protection.
- Works with any 12V batteries, including sealed, gel, and flooded.
- Advanced safety features such as overvoltage, overcurrent, low voltage, and short circuit protection are included.
- Simple installation and setup thanks to the provided user manual and accessories.

- Krieger 3000 Watt Power Inverter - 12V to 110V Modified Sine Wave Car Inverter.
- Hardwire Kit - for simple installation and a strong connection.
- DC to AC Converter - converts 12V DC power to 110V AC power.
- Installation Kit - includes all installation hardware.
- ETL Approved - complies with UL STD 458 safety standards.
3. Charge Controllers
Charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the batteries (if applicable). They prevent overcharging and ensure that the batteries are charged optimally.
4. Batteries (if applicable)
In some solar panel systems, batteries are used to store excess electricity for later use. These batteries are charged during periods when the the panels generate more electricity than is currently being consumed. They can be used to power the home or business during times of low sun exposure or at night.
5. Wiring
Wiring is essential for connecting all the components of a solar panel system. It ensures that electricity flows smoothly between the the panels, inverters, charge controllers, batteries, and the electrical system of the building.
6. Grounding
Grounding is a safety measure that protects the solar panel system and the building from electrical faults. It involves connecting the system to the ground to redirect any excess electrical current in the event of a fault or surge.
Understanding these components will give you a comprehensive knowledge of how the panels work and how each element contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
Solar Panel Sizing and System Design
When it comes to installing solar panels, one crucial aspect that needs to be considered is sizing and system design. This step ensures that your solar system is customized to meet your specific energy needs efficiently. To achieve this, several factors are taken into consideration:
Factors Considered for Sizing
- Energy needs: Determining your energy consumption patterns and understanding how much electricity your household or business requires is the first step in sizing your solar system.
- Roof space availability: The available space on your roof will directly impact the size and number of solar panels that can be installed. It’s essential to assess whether your roof has enough space to accommodate the desired system size.
- Geographical location: The amount of sunlight your location receives plays a vital role in sizing your solar panel system. Areas with more sunlight may require fewer panels compared to regions with less sunshine.
- Electricity consumption patterns: Analyzing your electricity usage throughout the day helps determine the optimal size of your solar panel system. Understanding peak hours and average consumption assists in designing a system that aligns with your specific energy requirements.
By considering these factors, the panel installers can design a system that maximizes efficiency while meeting your energy goals.
Read More on Container Pools in NZ – Unparalleled Backyard Beauty
Solar Panel Integration with the Grid
When considering solar panel systems, it’s essential to understand how they integrate with the grid. Here are some key points to know:
Grid-tied vs. Off-grid Systems
A grid-tied solar panel system is connected to the local utility grid. It allows you to benefit from both solar power and traditional grid electricity. In contrast, an off-grid system operates independently and requires batteries to store excess energy.
Net Metering
Net metering is a program offered by many utility companies. It allows homeowners to receive credit for the excess energy their panels generate. This credit can be used when their panels are not producing enough electricity, such as during nighttime.
Read More on What Is Net Metering? Easy Explanation
Feed-in Tariffs
Feed-in tariffs are another way homeowners can benefit from their solar panel systems. Under this program, utilities pay homeowners a fixed rate for every kilowatt-hour of electricity their panels produce. This incentivizes renewable energy production and helps reduce overall energy costs.
Connecting Solar Panels to the Grid
To connect solar panels to the grid, a licensed electrician typically installs an inverter. The inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with the grid. This ensures a seamless integration of solar power into your existing electrical system.
Environmental Impact of Solar Panels
As we explore the various aspects of solar panels, it is crucial to also understand their environmental impact. Solar panels have gained popularity due to their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
Life Cycle Analysis
Life cycle analysis is a comprehensive approach used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire life cycle.
When it comes to solar panels, life cycle analysis assesses the environmental effects associated with raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, installation, use, and eventual disposal.
By considering the entire life cycle, we can accurately gauge the carbon footprint and other environmental aspects of the panels, enabling us to make informed decisions about their adoption.
Recycling Methods
Solar panel recycling methods play a pivotal role in minimizing waste and ensuring the sustainable use of materials. Solar panels consist of valuable components, including silicon, aluminum, glass, and various metals.
Specialized recycling processes are employed to recover and reuse these materials, reducing the need for resource extraction and minimizing environmental impact.
Efforts are being made to establish efficient and scalable recycling infrastructures to handle the growing volume of decommissioned solar panels. Through responsible recycling, we can maximize the environmental benefits of using solar energy.
Read More on Luxury Container Hotels – Offering Unique Experiences
Comparison of Solar Energy with Other Energy Sources
Comparisons between solar energy and other conventional energy sources provide valuable insights into the environmental advantages of solar panels.
Traditional energy generation methods heavily rely on fossil fuels, releasing significant amounts of greenhouse gases and contributing to climate change.
In contrast, the panels produce clean energy without emitting harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. This significantly reduces air pollution, improves air quality, and mitigates the adverse environmental impact associated with conventional energy sources.
- Solar panels offer a sustainable solution for electricity generation, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- They contribute to the global efforts to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Solar energy helps protect ecosystems and preserves biodiversity by reducing pollution and habitat destruction caused by traditional energy generation methods.
Understanding the environmental impact of the panels is crucial for promoting sustainable energy practices and transitioning towards a greener future. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can make a positive impact on both the environment and our energy systems.
Recent Advancements in Solar Panel Technology
- Solar roof tiles
- Transparent solar panels
- Bifacial cells
- Perovskite-based panels
As technology continues to advance, so does the world of solar panel technology. In recent years, there have been exciting developments that have expanded the capabilities and possibilities of solar panels. These advancements have made solar panels more versatile, efficient, and aesthetically appealing.
Solar Roof Tiles

Solar roof tiles are a cutting-edge innovation in the world of solar energy. Unlike traditional solar panels that are mounted on top of a roof, solar roof tiles are integrated seamlessly into the roof itself.
This not only provides a more streamlined and attractive appearance, but also increases the efficiency of the the panels.
Solar roof tiles are made to resemble traditional roofing materials, such as tiles or shingles, making them a popular choice for homeowners who want to harness the power of the sun without compromising the aesthetic appeal of their home.
Transparent Solar Panels
Another remarkable advancement in solar panel technology is the development of transparent solar panels. These panels are designed to be see-through, allowing them to be integrated into windows, skylights, and other transparent surfaces.
This opens up a whole new realm of possibilities for solar energy integration, as buildings can now generate electricity without sacrificing natural light or obstructing views.
Transparent panels are a game-changer in architectural design, offering a unique combination of functionality and aesthetics.
Bifacial Cells
Bifacial cells are a type of solar cell that can generate electricity from both sides. Traditional solar cells only capture sunlight from one side, but with bifacial cells, the backside of the cell can also convert sunlight into electricity.
This results in increased energy production and efficiency, as the cell can harness sunlight that is reflected from the ground or surrounding surfaces.
Bifacial cells can be used in both rooftop and ground-mounted solar panel installations, making them a versatile and highly effective option.
Perovskite-based Panels
Perovskite-based panels are a relatively new type of solar panel that show great promise in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Perovskite is a type of material that can be used to create solar cells with high energy conversion efficiency.
These panels have the potential to be more efficient and cheaper to produce compared to traditional silicon-based panels. While perovskite-based panels are still being developed and perfected, they represent an exciting future for solar panel technology.
Read More on Experience Luxury Living In Tasmania With Stunning Container Homes
Solar Panels: Everything You Need to Know
Electricity: Basics of electricity and how solar panels produce electricity
Understanding the basics of electricity is essential to grasp how solar panels produce electricity. Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is generated through various sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewables like solar energy.
When it comes to solar panels, they rely on the photovoltaic effect to produce electricity. Photovoltaic cells, which are the building blocks of the panels, convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials.
How Do Solar Panels Produce Electricity?
1. Sunlight: Solar panels capture sunlight that contains photons (particles of light).
2. Photovoltaic Cells: The photovoltaic cells within the solar panel consist of a positively charged and negatively charged layer of silicon. When photons from sunlight strike these cells, electrons are released from their atoms.
3. Electric Field: An electric field is created within the photovoltaic cells due to the presence of the positive and negative layers of silicon. This electric field pushes the released electrons towards the positive side, creating a flow of electric charge.
4. Direct Current (DC): The flow of electrons results in the creation of direct current (DC) electricity.
5. Inverter: The generated DC electricity is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the type commonly used in homes and buildings.
6. Electrical System: The AC electricity produced by solar panels can be used to power electrical appliances and devices in your home. Any excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, earning credits or supplying electricity to other users.
By harnessing the power of sunlight, the panels provide a sustainable and clean way to produce electricity while reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Photovoltaic Cells: Explanation of How Photovoltaic Cells Work in Converting Sunlight into Electricity
Photovoltaic cells, also known as PV cells, are at the heart of solar panel systems. These small, semiconductor devices have the remarkable ability to convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
When sunlight hits the surface of a PV cell, the photons in the sunlight excite the electrons in the cell’s material, creating an electric field. This electric field then pushes the electrons to flow in a certain direction, creating a direct current (DC) of electricity.
Each PV cell consists of two layers of a specific material, usually silicon, sandwiched together to create a p-n junction. The top layer, known as the n-type layer, is doped with impurities to have an excess of negatively charged electrons.
The bottom layer, known as the p-type layer, is also doped but with impurities that create a deficit of electrons, resulting in positively charged holes.
When sunlight strikes the PV cell, the energy from the photons is sufficient to knock the electrons from the valence band of the silicon atoms in the n-type layer. These freed electrons are then attracted to the positive holes in the p-type layer, creating a flow of electrons from the n-type layer towards the p-type layer.
This flow of electrons is what generates the electric current, which can be harnessed and used to power various devices.
Not So Fast, You Can’t Use This Electricity Yet
However, before this electricity can be used in our homes or businesses, it needs to go through an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to match the electricity provided by the grid.
The efficiency of photovoltaic cells in converting sunlight into electricity has improved significantly over the years. With advancements in technology and understanding, research is ongoing to develop more efficient and cost-effective cells.
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are the key components of the panels, and their ability to convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect makes solar energy a viable and sustainable source of power.
Read More on Luxury Container Homes In South Africa: Incredible Concepts
Cost: Factors Influencing the Cost of Solar Panel Installation and Potential Savings
When considering installing solar panels, it’s important to understand the factors that can influence the cost of the installation as well as the potential savings you can achieve. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. System Size
The size of the solar panel system you choose will have a significant impact on the cost. Larger systems will typically cost more to install but can generate more electricity and savings in the long run.
2. Solar Panel Quality
The quality and efficiency of the solar panels you choose will also affect the overall cost. Higher quality panels may have a higher upfront cost but can provide better performance and durability, leading to greater savings over time.
3. Installation Complexity
The complexity of the installation can impact the cost. Factors such as the roof type, shading, and the need for additional equipment or structural modifications can increase the installation cost.
4. Incentives and Rebates
Government incentives and available rebates can help offset the cost of solar panel installation. Research the incentives and rebates available in your area to determine how they can contribute to your overall savings.
5. Financing Options
The financing options you choose can also influence the overall cost. Whether you opt for a cash purchase, loan, or lease agreement, understanding the terms and interest rates will help you determine the true cost of your solar panel system.
6. Energy Savings
One of the key benefits of solar panels is the potential savings on your electricity bills. By generating your own clean energy, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your monthly electricity costs, leading to long-term savings.
7. Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the return on investment is crucial in understanding the potential savings. Estimate the payback period based on the upfront cost and the projected savings over time to determine how quickly you can recoup your initial investment.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about the cost of solar panel installation and the potential savings you can achieve. Installing the panels can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly choice for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save money in the long run.
Read More on Are Container Homes Legal in Miami? Find Out the Facts!
Homeowner: Considerations for Homeowners When Deciding to Install Solar Panels
Evaluating Energy Needs
Before installing solar panels, homeowners should assess their energy needs. Factors to consider include the size of the household, energy usage patterns, and future energy requirements.
Roof Suitability
The suitability of the roof for solar panel installation is crucial. Factors such as the roof’s orientation, slope, and shading from nearby objects can impact the system’s efficiency. A professional assessment may be necessary to determine if the roof is suitable.
Financial Considerations
Homeowners should evaluate the financial aspects of installing solar panels. This includes considering the upfront costs, potential tax credits or rebates, and long-term savings on electricity bills. It is advisable to consult with a financial expert to assess the financial feasibility.
Maintenance and Warranty
Understanding the maintenance requirements of solar panels is essential. Homeowners should inquire about warranties, expected lifespan, and any regular maintenance tasks required to ensure optimal performance.
Permitting and Regulations
When installing solar panels, homeowners must adhere to local permitting and regulations. It’s crucial to familiarize oneself with the necessary permits, codes, and restrictions applicable in their area.
Insurance and Liability
Homeowners should check their insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for the solar panel system. Additionally, it is important to understand the liability implications in case of any damage or accidents related to the installation.
Choosing a Qualified Installer
The expertise and reputation of the installer play a vital role in the success of a solar panel installation. Homeowners should carefully research and select a qualified installer with relevant certifications and experience.
Read More on Shipping Container Homes In Arizona: Stylish And Affordable
Solar Panel Installation on the Roof: Steps and considerations for Installing Solar Panels on Various Types of Roofs
Installing solar panels on your roof is a great way to harness the power of the sun and reduce your reliance on traditional energy sources.
Whether you have a flat roof, a pitched roof, or a metal roof, the installation process will involve a few key steps and considerations.
1. Roof Inspection
The first step in installing solar panels on your roof is to conduct a thorough inspection. This will help determine if your roof is suitable for the panel installation. Factors to consider include the age and condition of your roof, the amount of shade it receives, and the structural integrity.
2. Roof Orientation and Tilt
The orientation and tilt of your roof play a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of your solar panels. Ideally, your roof should be south-facing and have a tilt angle that matches your geographical location. This will ensure that your panels receive optimal sunlight throughout the day.
3. Roof Reinforcement
Depending on the weight and size of the solar panels, your roof may need reinforcement to bear the additional load. This is especially important for older roofs or those with a weak structure. Consulting with a professional installer can help determine if reinforcement is necessary.
4. Electrical Wiring
Once your roof is deemed suitable for solar panel installation, the next step is to install the electrical wiring. This includes connecting the panels to an inverter, which converts the DC power generated by the panels into AC power for use in your home.
5. Mounting the Panels
Mounting the solar panels securely on your roof is crucial to ensure their long-term stability and performance. There are various mounting options available, including roof-mounted and ground-mounted systems. The type of mounting system will depend on your roof type and available space.
6. Permits and Regulations
Before installing solar panels on your roof, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the local permits and regulations. Some areas may require building permits or follow specific guidelines for the panel installation. It’s crucial to comply with these regulations to ensure a smooth and legal installation process.
7. Maintenance and Monitoring
Once your solar panels are installed, regular maintenance and monitoring are key to keeping them functioning optimally. This includes cleaning the panels, checking for any damage or obstructions, and monitoring the energy production to identify any potential issues.
Read More on Shipping Container Homes In Oklahoma: Stylish and Sustainable
To Tie it Up
Installing solar panels on your roof can be a rewarding investment both for the environment and your energy savings. By following these steps and considering the unique aspects of your roof, you can embark on a successful solar panel installation journey.
Saving Money with Solar Panels: How Solar Panels Can Lead to Long-term Cost Savings for Homeowners
In today’s world, where the cost of traditional energy sources keeps rising, finding ways to save money has become a top priority for homeowners.
One solution that has gained significant attention is installing solar panels. Not only do the panels help you to reduce your carbon footprint, but they also offer remarkable long-term cost savings.
Here’s how solar panels can lead to cost savings for homeowners:
1. Reduced Electricity Bills
One of the primary ways solar panels save you money is by reducing your dependence on the grid. The panels harness the power of the sun to generate electricity for your household.
By using the electricity your panels generate, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your monthly electricity bills.
Imagine the relief of not having to worry about rising energy costs or adjusting your budget to accommodate increased electricity prices. Solar panels provide homeowners with a reliable and renewable energy source, helping them save money on their electricity bills for years to come.
2. Net metering
Net metering is another way in which solar panels can lead to long-term cost savings. This system allows homeowners to earn credits for any excess electricity their solar panels produce but do not consume.
These credits can then be used to offset the electricity consumed during times when the panels aren’t generating enough energy, such as at night or during cloudy days.
With net metering, homeowners can effectively store the energy produced by their panels and utilize it when they need it the most. This not only helps to reduce your electricity bills further but also increases the financial benefits of going solar.
Read More on How Much Is A Container Home in Florida? Your Ultimate Guide
3. Increased Home Value
Investing in solar panels doesn’t just save you money on your monthly bills; it can also increase the value of your home. Studies have shown that homes equipped with the panels tend to sell at a higher price compared to homes without solar installations.
This increased home value can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, potential buyers are attracted to the idea of owning a home with lower energy costs, which is becoming increasingly important in today’s environmentally conscious society. Secondly, solar panels offer long-term savings, making the property more desirable.
Therefore, by installing solar panels, you not only save money while you live in your home but also potentially make a profit when and if you decide to sell.
4. Tax Incentives and Rebates
Lawmakers and governments worldwide understand the importance of transitioning to renewable energy sources. As a result, many countries, states, and municipalities offer significant tax incentives, grants, and rebates for homeowners who install solar panels.
These incentives can help offset the upfront costs of installing the panels, making it even more affordable for homeowners to go solar. By taking advantage of these programs, homeowners can save thousands of dollars on their solar panel installations, accelerating their return on investment.
Furthermore, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the United States allows homeowners to claim up to 26% of the total cost of their solar energy systems as a tax credit. This substantial benefit further contributes to the long-term cost savings that the panels offer.
In conclusion, solar panels offer homeowners an incredible opportunity to save money in the long run. With reduced electricity bills, net metering, increased home value, and various incentives and rebates, the cost savings potential is substantial. Considering the benefits and long-term savings they provide, solar panels are undoubtedly a wise investment for homeowners.
Solar Panels in the US: Information Specific to Solar Panel Installation and Regulations in the United States
Installing solar panels in the United States has become increasingly popular in recent years, as more and more homeowners recognize the benefits of harnessing solar energy.
However, before embarking on a panel installation project, it’s important to understand the specific regulations and guidelines that apply to the United States.
Solar Panel Installation Regulations
Each state in the US has different regulations and requirements for solar panel installation. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your state before proceeding with the installation process. Some common regulations to consider include:
- Building permits: In many states, you will need to obtain a building permit before installing solar panels on your property. This ensures that the installation meets safety and structural requirements.
- Net metering: Net metering is a billing arrangement that allows homeowners to receive credit for the excess electricity they generate and feed back into the grid. Understanding your state’s net metering policy is important for maximizing the financial benefits of solar panels.
- Interconnection standards: Interconnection standards dictate the technical requirements for connecting solar panel systems to the electric grid. It’s essential to comply with these standards to ensure a safe and efficient integration.
Financial Incentives and Rebates
The US government, along with many state and local governments, offer various financial incentives and rebates to encourage solar panel adoption. These incentives can significantly offset the upfront costs of installation and make going solar more affordable. Some of the common incentives include:
- Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC): The ITC allows homeowners to deduct a portion of their solar panel installation costs from their federal taxes. It currently offers a 26% tax credit but is subject to change in the future.
- State and local incentives: Many states and local governments provide additional incentives such as rebates, grants, or property tax exemptions for solar panel installations.
Local Solar Panel Installers
When considering solar panel installation, it’s crucial to work with a reputable and experienced local panel installer. They have the knowledge and expertise to navigate the local regulations and ensure a smooth installation process. Look for installers who are licensed, insured, and have positive customer reviews.
In conclusion, before installing solar panels in the US, it’s essential to understand the specific regulations, incentives, and find a reliable installer. By doing so, you can ensure a successful installation that maximizes the benefits of solar energy for your home and the environment.
Need for Solar Panels: The Importance of Transitioning to Solar Energy and the Benefits It Offers
In today’s world, the need for alternative sources of energy has become increasingly crucial. As traditional energy sources such as fossil fuels continue to deplete, it is essential for us to transition to sustainable and renewable energy solutions. Solar panels play a vital role in this transition, providing numerous benefits for individuals and the planet as a whole.
One of the primary reasons why transitioning to solar energy is important is its positive environmental impact. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy does not produce harmful emissions or pollutants that contribute to air pollution and climate change.
By harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels significantly reduce our carbon footprint and help combat global warming. Furthermore, solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning we can continue to harness its power indefinitely without depleting its source.
Another key benefit of solar panels is the substantial cost savings they offer. Traditional electricity bills can be a significant financial burden, especially in the long run. By installing panels, homeowners can significantly reduce or even eliminate their dependence on the grid, resulting in substantial savings on energy costs.
Additionally, some governments and utility companies offer incentives and rebates for installing solar panels, making the initial investment even more affordable.
Moreover, panels provide energy independence. Relying solely on the grid leaves us vulnerable to power outages and price fluctuations in electricity.
By generating our own electricity through solar panels, we can ensure a constant and reliable source of power no matter the circumstances. This independence gives homeowners peace of mind and reduces their reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Why Transition to Solar Power
Transitioning to solar energy also creates job opportunities and stimulates the economy. The solar industry has experienced rapid growth in recent years, creating numerous employment opportunities across the globe.
By investing in panels, individuals contribute to the expansion of this industry, supporting local economies and driving innovation in clean energy technology.
In conclusion, the need for panels is undeniable. Transitioning to solar energy offers a multitude of benefits, including environmental preservation, significant cost savings, energy independence, and economic growth.
By embracing solar power, we not only secure a sustainable future for ourselves but also contribute to the betterment of the planet and future generations.
Read More on Shipping Container Homes in Oregon: Sustainability And Style


Andu Green
Tuesday 10th of January 2023
This is wonderful information.
homesolarwind
Thursday 9th of March 2023
Glad we could help. Thanks for stopping by.